Home >> Pelviureteric junction obstruction
What is Pelviureteric junction obstruction(PUJO) and how it is treated?
The traditional treatment for ureteropelvic junction obstruction has been open surgery (open pyeloplasty) to cut out the area of narrowing and re-connect the ureter to the kidney.
The traditional treatment for ureteropelvic junction obstruction has been open surgery (open pyeloplasty) to cut out the area of narrowing and re-connect the ureter to the kidney.


What is Pelviureteric junction obstruction(PUJO)?
The ureter is a long thin tubular structure 10-12 inches long which carries urine produced in the kidney to the bladder. The urine is actively propelled by the muscular ureter down into the bladder by a process called peristalsis.
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction is a condition where blockage occurs at the junction where the ureter attaches to the kidney. This results in decreased flow of urine down the ureter and an increase of fluid pressure inside the kidney. This can result in kidney damage.
The ureter is a long thin tubular structure 10-12 inches long which carries urine produced in the kidney to the bladder. The urine is actively propelled by the muscular ureter down into the bladder by a process called peristalsis.
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction is a condition where blockage occurs at the junction where the ureter attaches to the kidney. This results in decreased flow of urine down the ureter and an increase of fluid pressure inside the kidney. This can result in kidney damage.
What are symptoms produced by PUJO?
Ureteral obstruction can cause flank pain on the effected side sometimes with vomiting or rarely with urinary infection.
Investigations
Ultrasound can show kidney swelling( called hydronephrosis). Intravenous pyelography (IVP), CT scan and renal scan can be used later for diagnosis
Ureteral obstruction can cause flank pain on the effected side sometimes with vomiting or rarely with urinary infection.
Investigations
Ultrasound can show kidney swelling( called hydronephrosis). Intravenous pyelography (IVP), CT scan and renal scan can be used later for diagnosis
What are the newer treatment options for PUJO?
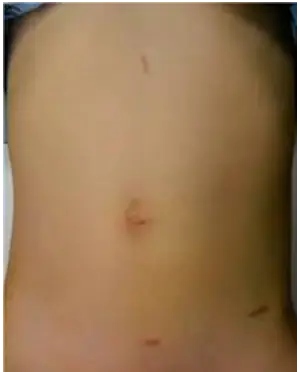
Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty was developed in order to give the same high success rate obtained with open pyeloplasty while decreasing the morbidity. The procedure is performed in the same manner as the open surgery, but through keyhole incisions without the need for a large scars. Postoperative pain is less, recuperation is significantly quicker and scarring is minimal when compared with open surgery. The procedure requires a general anesthesia and hospitalization (usually 2 nights). An internal stent tube is also needed for four weeks. Success with this procedure is the same as open surgery (>90%)
Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty was developed in order to give the same high success rate obtained with open pyeloplasty while decreasing the morbidity. The procedure is performed in the same manner as the open surgery, but through keyhole incisions without the need for a large scars. Postoperative pain is less, recuperation is significantly quicker and scarring is minimal when compared with open surgery. The procedure requires a general anesthesia and hospitalization (usually 2 nights). An internal stent tube is also needed for four weeks. Success with this procedure is the same as open surgery (>90%)